Is the strength of aluminum alloy power tool parts die casting sufficient to meet the requirements of high-load operations?
03-06-2025Basic strength characteristics of aluminum alloy parts under die-casting process
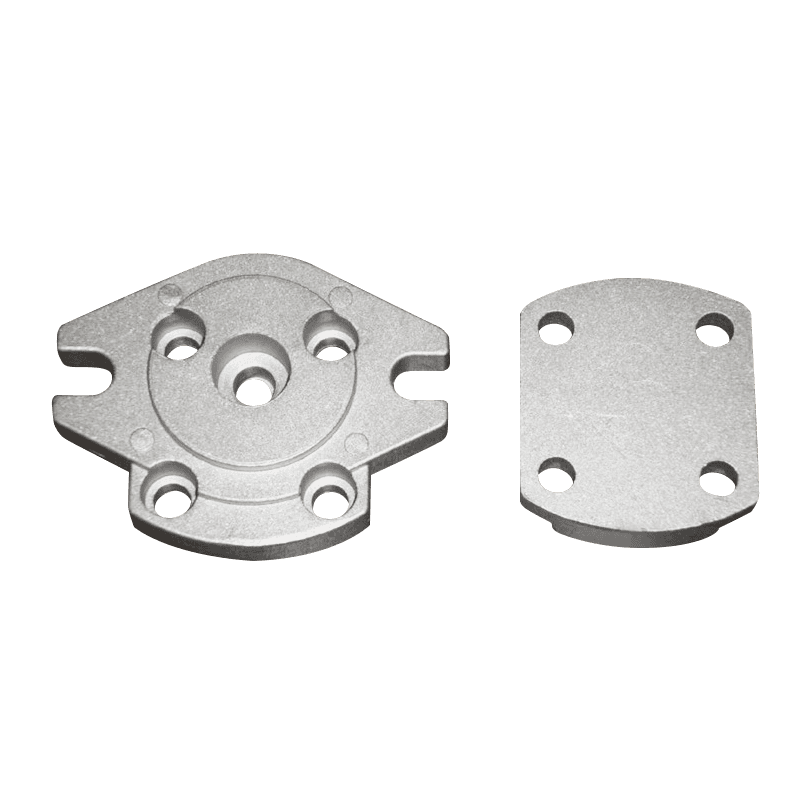
Aluminum alloy die-castings are widely used in power tool housings and internal structural parts due to their low density, light structure, and high molding efficiency. Common materials such as ADC12, A380, AlSi9Cu3, etc. have good tensile strength and impact resistance. Although the absolute strength of aluminum alloy is lower than that of forged steel or stainless steel, the load-bearing gap can be compensated by wall thickness distribution, rib arrangement, etc. during design. For the housing, protective structure or pressure-bearing parts of power tools, their basic strength can meet the mechanical requirements required for daily use.
The influence of structural design and force distribution on strength performance
Die castings need to consider structural uniformity and stress dispersion principles during design. Stress concentration can be reduced by reinforcing ribs, support ribs or fillet transitions, thereby improving the overall load-bearing capacity. Die-cast parts in power tools usually need to withstand intermittent vibration, high-frequency rotation and reaction force impact. Therefore, reasonable structural design is not only the key to improving load-bearing performance, but also directly related to the stability of parts during use.
The influence of die-casting molding quality on strength consistency
If shrinkage holes, pores, cold shuts and other defects occur during the die-casting process, the compactness of the internal structure of the parts will be affected, resulting in a decrease in local strength. To ensure the quality of die-casting parts, key process parameters such as mold temperature, alloy pouring speed, exhaust system and mold design need to be controlled. Finished parts usually need to be verified by X-ray detection, metallographic analysis or mechanical testing to verify their strength distribution. In mass production, the controllability of the die-casting process is of great significance to ensure the consistency of overall strength.
Application boundaries suitable for high-load scenarios
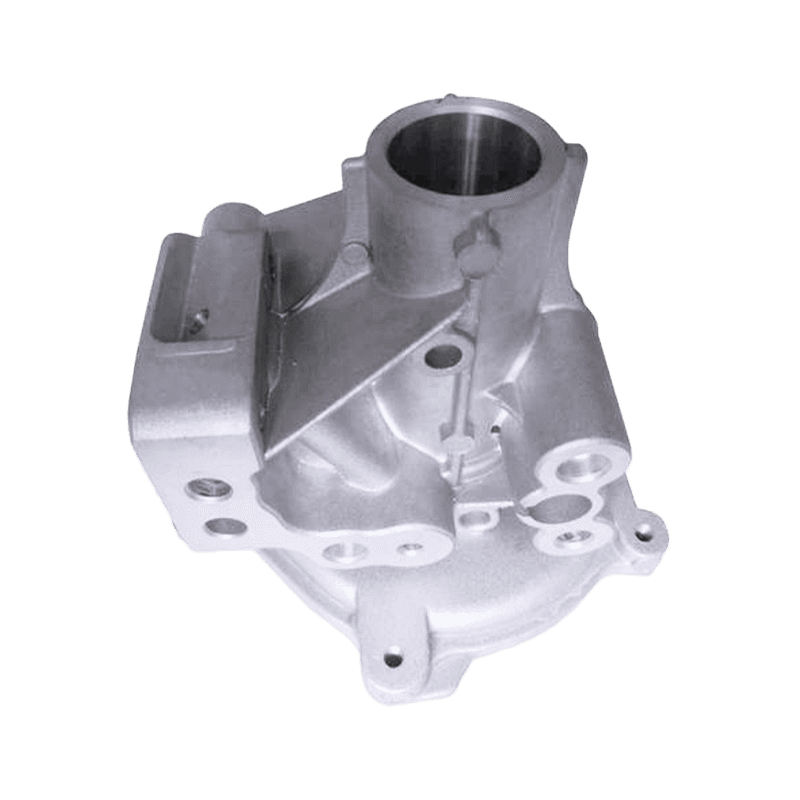
Although die-cast aluminum alloy parts are widely used in the transmission housing, front guard plate, gear cavity and other parts of power tools, some structures may still face insufficient strength or deformation problems under high-frequency, high-impact and high-temperature environments. For example, heavy industrial drilling machines, impact wrenches and other high-intensity operations and long working cycles place higher requirements on the fatigue performance of parts. In such scenarios, it is often necessary to match reinforced aluminum alloy materials or improve mechanical properties through heat treatment, infiltration and other methods.
Combined with post-processing process to optimize strength performance
In order to further improve the strength, aluminum alloy die castings often use T5 or T6 heat treatment process to precipitate and harden the Si and Cu elements in the organization. At the same time, some key parts will be supplemented by mechanical processing to ensure the connection accuracy and mechanical stability. In terms of surface treatment, processes such as anodizing and electrophoretic coating not only help to improve corrosion resistance, but also provide certain buffering protection against external force impact.
Application performance in actual cases
In actual product applications, such as a certain model of handheld angle grinder, its front shell uses ADC12 die casting. It has been verified that this structure can run stably for hundreds of hours in a high-speed vibration environment without obvious cracks or deformation. In addition, in the shell structure of high-frequency disassembly and assembly electric wrenches, die-cast aluminum alloys are also widely used, and the requirements of torsion and compression resistance are met through the control of rib position and thickness ratio.
Are You Interested In Our Products
Leave your name and email address to get our prices and details immediately.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 Deutsch
Deutsch русский
русский